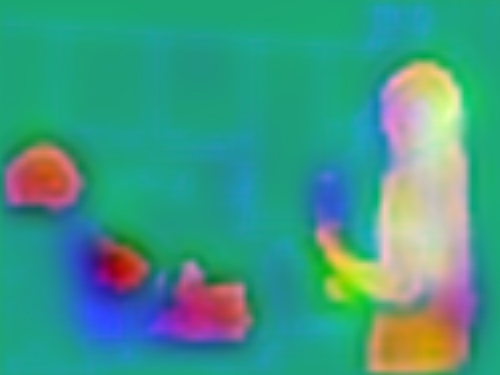
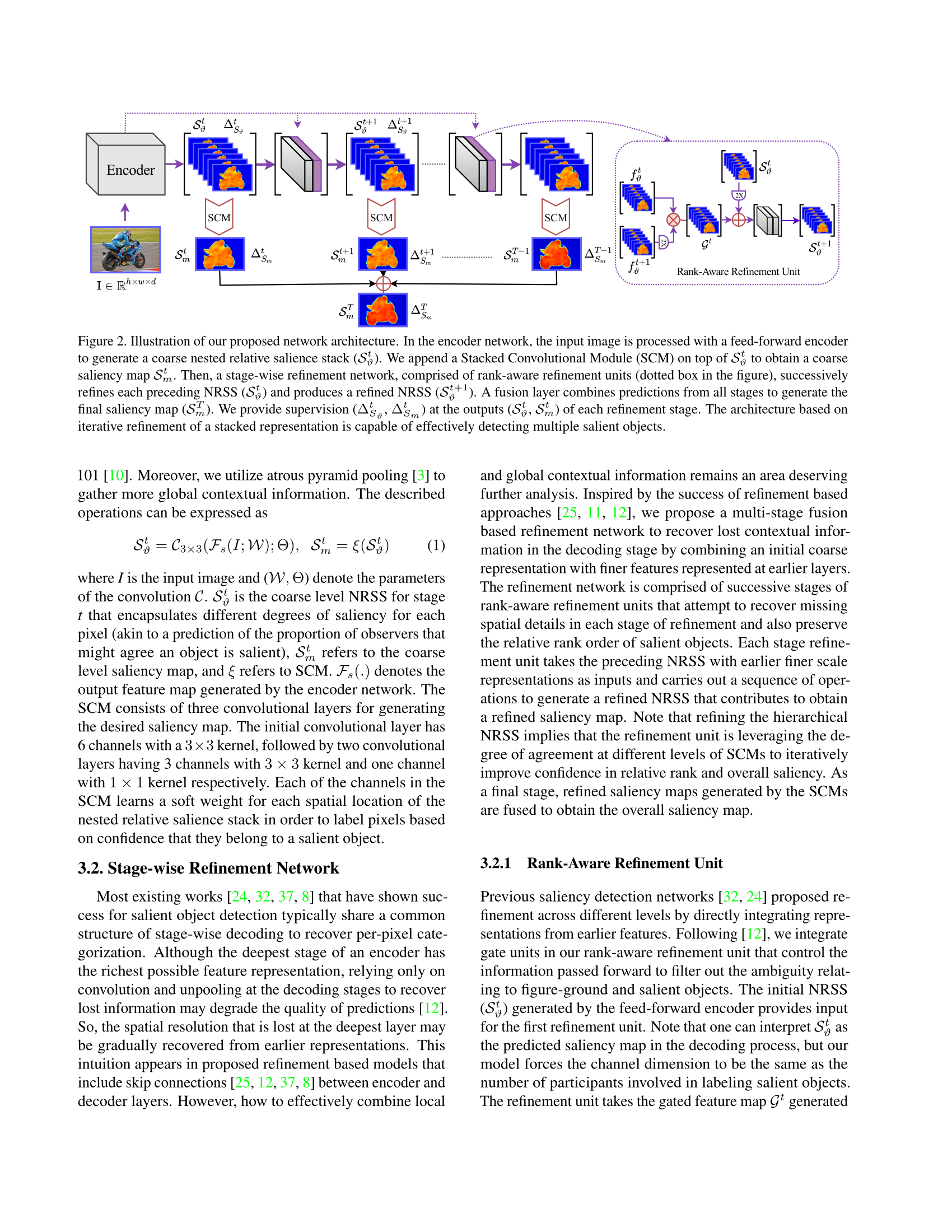
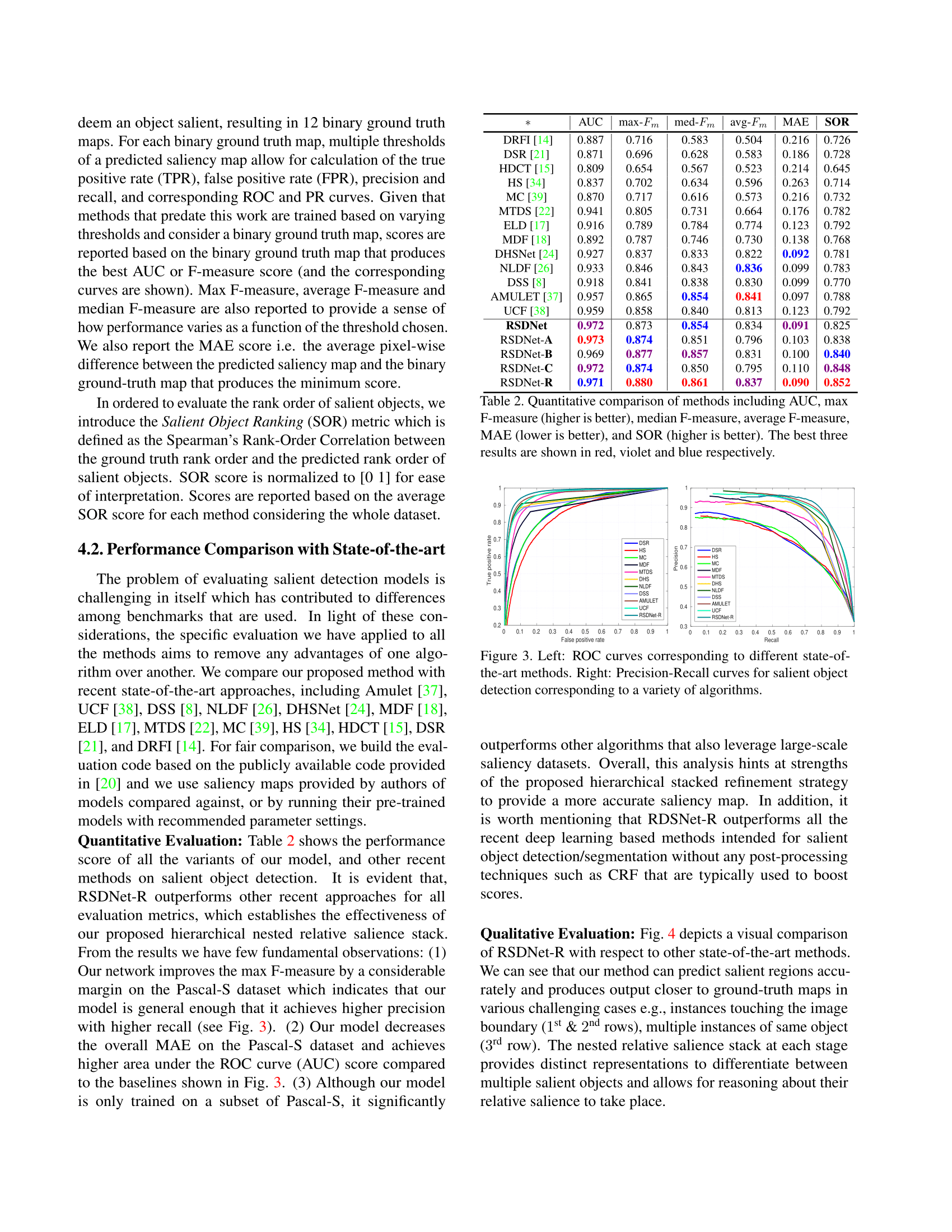
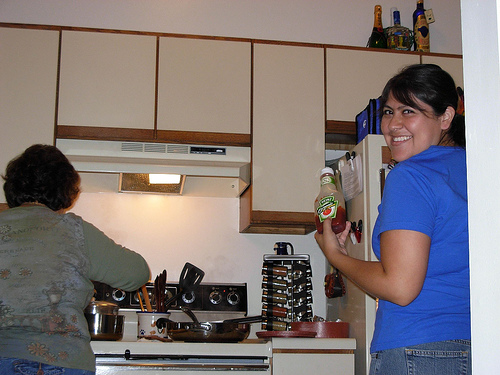Md Amirul Islam*, Mahmoud Kalash*, Neil D. B. Bruce
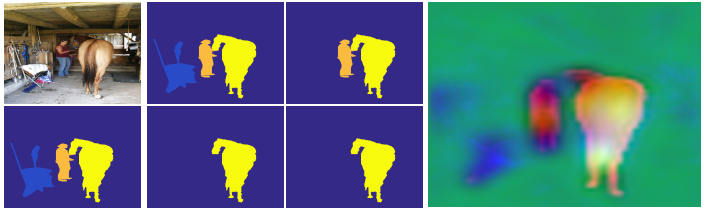
Revisiting Salient Object Detection: Simultaneous Detection, Ranking, and Subitizing of Multiple Salient Objects, CVPR, 2018. (Oral)
[BibTeX] [PDF]
Revisiting Salient Object Detection: Simultaneous Detection, Ranking, and Subitizing of Multiple Salient Objects, CVPR, 2018. (Oral)
[BibTeX] [PDF]
@inproceedings{islamsal18,
author = {A. Islam, M. Kalash, N. D. B. Bruce},
title = {Revisiting Salient Object Detection: Simultaneous Detection, Ranking, and Subitizing of Multiple Salient Objects},
booktitle = {Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR)},
year = {2018}
}